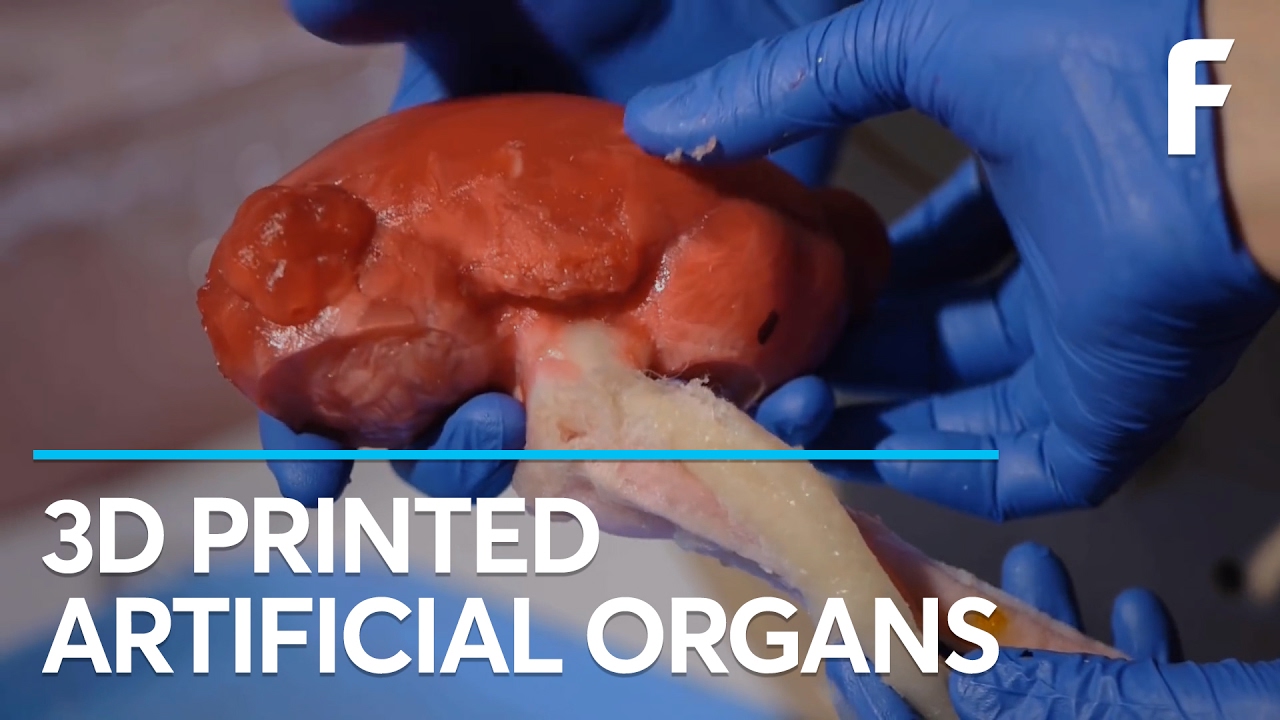
3d printing artificial organs
MSI PI Michael McAlpine associate professor Mechanical Engineering is the lead researcher on a recent project to use 3D printing technology to create artificial models of organs. 3D printing is a technology for the additive manufacturing of objects ie adding material layer by layer starting from digital three-dimensional models.

Artificial And Implantable Organs 5 Discoveries That Will Change The Future Of Organ Transplants Time Com
3D Artificial Kidney.

. Bioprinted tissue constructs containing human bone marrow MSCs surrounded by connective tissue and supported by an artificial endothelium-lined vasculature allowed the circulation of bone growth factors and subsequently the induction of bone. But 3D printing may help change the ground reality for Indians who need an organ transplant. One gentleman on Quora said that 3D printing is an attempt to reproduce physical objects artificially building it layer by layer.
Therefore it is possible to create real pancreas-mimic artificial organ for clinical application. The shape of the artificial organ often depends on the viscosity of. However costs toward medical applications in 3D printing are expected to grow to 21 in the next 10 years 19 billion out of an 89 billion industry.
3D-printed thick vascularized tissue constructs for organ engineering and regenerative medicine. Imagine being able to understand and see the complex structures of human organs at the cellular level. Living tissue has been successfully printed with a 1000 3D printer while more specialized bioprinters cost upwards of 100000.
Organ regeneration is best defined as the regrowth of lost tissues or organs in the response to injury. Elizabeth Montalbano Jan 04 2018. Pros of 3D organ printing include use in organ transplantation tissue repair for teaching purposes in disease and pharmaceutical research and reduction of organ trafficking.
You give the printer an image 3D representation of a specific object to see if it printable. It promises to revolutionize many areas including the medical field because of the high flexibility for the production of medical devices and artificial organs. In 2008 a 3D printer cost about 15000.
On February 13 a group of. These models can be used by surgeons to plan and practice for surgery. Researchers used 3D-printing to create human liver tissue that could soon be tested on the International Space Station.
By Jenny Tang. Lets discuss the pros and cons of 3D organ printing. The potential use of printers in this process was pioneered in 2000 by Thomas Boland a researcher then at Clemson University who filled the ink tanks of.
In conclusion 3D bioprinting can become a new leader in the development of the artificial pancreas to overcome the existed islet. Through artificial means however we can generate organs through 3D printing. 3D printing already is being used in medicine to provide physician guidance for how to treat actual.
According to The National Foundation for Transplants the average kidney transplant costs upwards of 300000 in contrast to the 3D bioprinter the printer used to create 3D printed organs can cost as little as 10000 and costs are expected to drop further as the technology evolves over the coming years. The paper can be read on the website of the journal. It is a naturally occurring phenomenon in certain organisms but in humans only few organs such as the liver and skin are known to be able to redevelop.
3D printing is a computer controlled technology in which the matter is combined and formed in a 3D form. Now consumers are able to purchase a 3D printer for just 300-1000 and download the software for designing objects. NASA astronaut Jessica Meir uses the BioFabrication Facility onboard the.
Using the powers of 3D printing scientists have been able to create artificial human tissue for quite some time now but now there may finally be some respite in terms of delivery. A team of researchers led by the University of Minnesota have 3D-printed lifelike artificial-organ models that mimic the exact anatomical structure mechanical properties and look and feel of real organs. The cost of 3D printing organs is changing as technology evolves.
A 3D-printed organ would have many applications especially in the healthcare industry. It goes like this. 3D Printing of Artificial Organs.
Were now a step closer to 3D printing organs meant solely for transplant. Furthermore constructing a vascularization of the artificial pancreas is actualized with 3D bioprinting.

Replacement Parts Engineering Pigs Growing Organs In The Lab Or 3d Printing Them Amazing Science

Eth Zurich 3d Prints A Beating Artificial Heart Artificial Heart 3d Printing 3d Printed Heart

Rit 3d Bioprinting Searches For Materials To Help The Body Repair Itself 3d Printing Industry

Researchers Developing Gelatin Bio Ink To 3d Print Human Tissues And Organs 3d Printing 3d Printing Technology 3d Printing Business

3d Printing A Better Socket For Prosthetic Limbs 3d Printing Prosthetics 3d Printer

Inventor Of The Segway Dean Kamen Now Wants To Build Factories For Lab Grown Human Organs Which Would Help The 110 617 P Human Tissue 3d Printing Human Organ

3d Printed Organs From Regenerative Living Cells Regenerative Medicine 3d Printing 3d Printing Technology

The Evolution Of 3d Printing Past Present And Future 3d Printing Industry

Switzerland Has Often Been The Heart Ha No Pun Intended Of Design And Build They Re At It Again And Have Crea Artificial Heart 3d Printing 3d Printed Heart

3d Printed Organs From Regenerative Living Cells 3d Printing 3d Printer 3d Printing Business

Pin On What In The World Is Going On

Artificial Human Austrian Laboratory 3d Prints Placenta In Bizarre Experiment Human Embryo Human Human Placenta

3d Printing Helps Eth Zurich Scientists Create Beating Silicone Heart Artificial Heart 3d Printed Heart 3d Printing

Developing A Universal Bioink Collplant Joins Remdo Biomanufacturing Initiative 3dprint Com The Voice Of 3d Printing Additive Manufacturing 3d Printing Development Health Care